Qu’est-ce qu’un matériau biosourcé ?
Entre l’entrée en vigueur de législations environnementales plus ambitieuses et le recours aux matières premières d’origine fossiles de plus en plus coûteux, les matériaux biosourcés connaissent une forte croissance.
L’utilisation de matériaux biosourcés a connu une forte hausse au cours des dernières années. Aujourd’hui, on estime que le la fibre végétale représente entre 5 et 10% du marché des isolants.
Définition d'un matériau biosourcé
Les matériaux biosourcés sont issus de la matière organique renouvelable (biomasse), d’origine végétale ou animale. Au-delà de leur utilisation principale dans les matériaux et produits de construction, on retrouve également leur utilisation en tant que produits de décoration, dans l’habillement, dans l’emballage ou encore dans le mobilier fixe.
Les matériaux biosourcés font partie de la famille des écomatériaux, complétée par les matériaux géosourcés. Ces derniers sont des matériaux d’origine minérales ou premières, qui demandent peu de transformation (terre crue, pierre).
Quels sont les principaux matériaux biosourcés ?
On compte sept principaux types de matériaux :
- La laine de mouton : il s’agit en général de laine impropre pour l’industrie textile. Son utilisation permet de produire des rouleaux ou panneaux, la laine en vrac et les écheveaux.
- Le bois : utilisé depuis très longtemps dans la construction, il permet la création de produits de constructions tels que les structures porteuses, le bardage, les menuiseries, les panneaux de bois, la laine de bois, le bois en vrac.
- Le chanvre : plante à croissance rapide nécessitant pas ou peu d’engrais. La fibre et la chènevotte en sont les parties les plus répandues pour le secteur du bâtiment. Le chanvre est utilisé pour créer des mortiers, des enduits, du béton et la laine de chanvre, ou peuvent être directement utilisées en vrac.
- La ouate de cellulose : issue du papier recyclé, elle permet la création de panneaux semi-rigides ou peut être utilisée directement en vrac.
- Le liège : réalisée principalement grâce au chêne-liège ou par le recyclage des bouchons, cette matière permet par exemple la création de panneaux et rouleaux recyclés.
- La paille : largement disponible sur le territoire français, elle peut être utilisée dans la construction sous forme de bottes, panneaux et enduit.
- Le textile recyclé : récupérés dans les chutes de l’industrie textile et les bennes de tris. Après traitement (découpage, hachage, défibrage, thermo-liaison avec du polyester), il est utilisé pour former des rouleaux ou panneaux semi-rigides.
Quel est l’intérêt de l’utilisation des matériaux biosourcés dans la construction ?
Ces matériaux biosourcés sont bien plus efficients du point de vue environnemental que les matériaux traditionnels d’origine fossile. Selon une étude réalisée par le Hub des prescripteurs bas carbone, en substituant des matériaux d’origine fossile par du biosourcé il serait possible de diminuer jusqu’à 60% de l’impact carbone d’un grand nombre de produit : cloisonnements, bardages, portes, fenêtres, revêtements de sols durs, revêtements muraux, isolants, etc.
Quelles mesures et législations encouragent le recours au biosourcé dans la construction ?
La loi n° 2015-992 du 17 août 2015 relative à la transition énergétique pour la croissance verte prévoit les dispositions suivantes :
« Toutes les nouvelles constructions sous maîtrise d’ouvrage de l’État, de ses établissements publics ou des collectivités territoriales font preuve d’exemplarité énergétique et environnementale et sont, chaque fois que possible, à énergie positive et à haute performance environnementale » (article 8 I).
En 2018, La loi Elan (Evolution du Logement, l’Aménagement et le Numérique) précise que dans le domaine de la construction ou de la rénovation de bâtiments publics, il faut également prendre en compte les exigences de lutte contre les émissions de gaz à effet de serre et de stockage du carbone et veiller au recours à des matériaux issus des ressources renouvelables. Elan impose plusieurs mesures afin de favoriser le recours au biosourcé :
- Introduction de la préfabrication (dispositif constructif largement utilisé en bois construction) dans le code de la construction et de l’habitation ;
- Annonce de mesures en faveur de la construction de maisons individuelles préfabriquées ;
- Annonce d’une réglementation environnementale en 2020 qui devra prendre en compte le stockage de carbone dans les matériaux de construction que les matériaux biosourcés permettent.
Le label Bâtiment biosourcé permet de valoriser l’utilisation des matériaux biosourcés dans la construction. Il définit un cadre réglementaire, d’application volontaire. Ce label définit plusieurs niveaux d’exigence quantitatifs – c’est-à-dire en fonction du volume de matériaux utilisés – et qualitatifs – utilisation de FDES (fiches de déclarations environnementales et sanitaires) plutôt qu’à des DED, recours au bois issu de forêts gérées durablement, assurer une faible émission de composés organiques volatils -.
Enfin, la Réglementation Environnementale 2020, entrée en vigueur le 1er janvier 2022 positionne les matériaux biosourcés comme solutions prioritaires, voire inéluctables, pour un futur éco-responsable dans les constructions neuves, tant en logements qu’en bâtiments tertiaires. Le choix notamment du recours à l’ACV Dynamique dans le calcul de l’Analyse du Cycle de Vie Bâtiment favorise le recours à ce type de matériaux.
Quels sont les principales difficultés à l’adoption et à la généralisation des matériaux biosourcés ?
Au niveau de la production : ces produits manufacturés sont normés, et ne posent pas de problème du point de vue technique et savoir-faire. En revanche, la capacité industrielle française est pour le moment insuffisante pour répondre à la demande des acteurs de la construction, en très forte hausse au cours des dernières années. Ceci contribue également au fait que les prix de ces matériaux sont pour le moment supérieurs aux matériaux minéraux et fossiles traditionnellement utilisés.
Leur utilisation demande des savoir-faire particuliers, et sont soumis à des normes de montage et de mise en œuvre qui doivent être encadrées et faire l’objet de contrôles techniques. Les risques en cas de mauvaise pose ou d’utilisation incorrecte peuvent être une plus forte sensibilité à l’humidité ou des risques d’incendies accrus. Néanmoins, la filière a rapidement su monter en compétences sur ces sujets, s’accaparer et maîtriser des systèmes complexes et prendre en compte les défauts et les qualités de chaque produit.
Pour finir, il reste un fort besoin de sensibilisation, d’information et de formation de la filière de la construction, plus particulièrement autour des maîtrises d’ouvrages, autour de l’utilisation de ces matériaux. Ceux-ci doivent être encadrés et conseillés sur les projets pouvant accueillir des matériaux et produits biosourcés et sur les usages possibles
Découvrez nos logiciels Vizcab pour certifier et labéliser vos projets de construction bas carbone
De la phase de diagnostique et faisabilité à la phase d’exécution d’un projet de construction, nous vous proposons des logiciels adaptés pour chaque professionnel pour bâtir votre stratégie bas carbone.

En phase amont
Dès l'esquisse, sécurisez l'objectif coût / carbone de vos projets.
Optimisez votre rentabilité d’un projet en jouant sur les paramètres les plus impactants pour atteindre vos objectifs et fédérez les acteurs grâce à des supports de communication percutants.
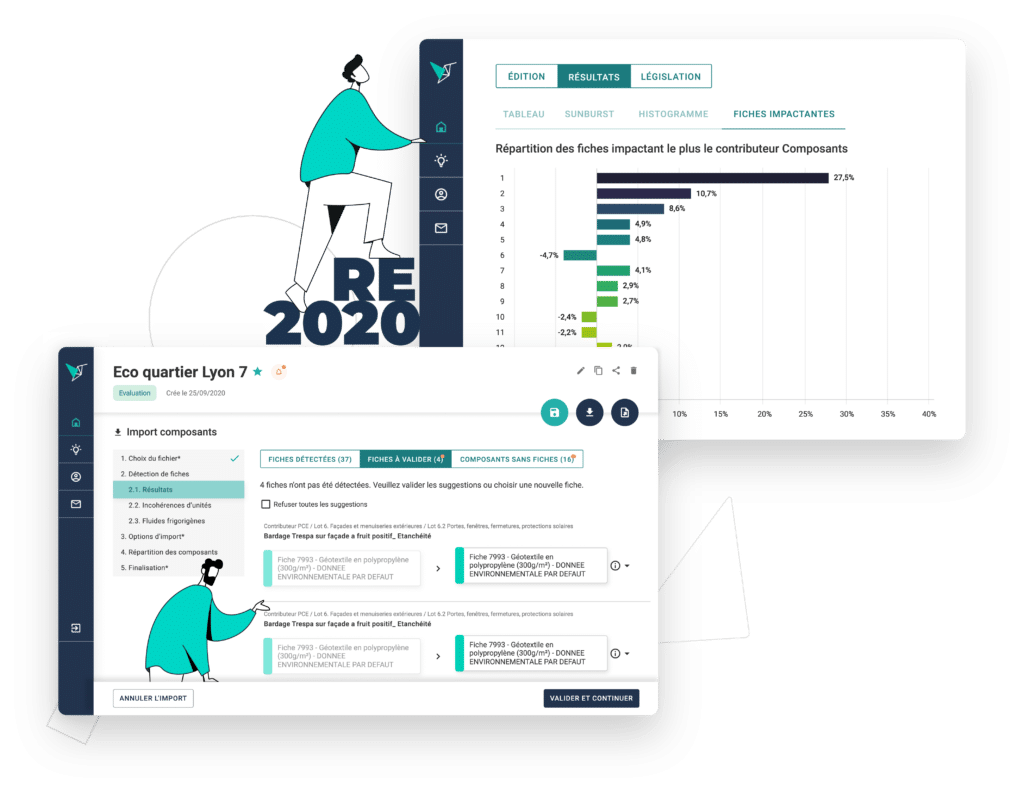
En phase aval
Calculez et optimisez l'impact environnemental de vos projets
Vizcab Eval la solution pour vous permettre de produire des études ACV bâtiment fiables, robustes et percutantes en un minimum de temps.
